The total variable cost TVC curve slopes up at an accelerating rate reflecting the law of diminishing marginal returns. B multiplied by fixed costs.
In the short-run at least one factor of production is fixed so firms face both fixed and variable costs.
If production increases by 25%, how will total fixed costs likely react?. Decrease by 25 D. For example suppose a company leases office space. The short run as economists use the phrase is characterized by.
The shape of the cost curves in. D Decreasing average fixed costs. The relevant range of the cost B.
The company absorbs overheads on a machine hour basis. Total fixed costs remain the same within the relevant range. Average cost can be influenced by the time period for production increasing production may be expensive or impossible in the short run.
A At least one fixed factor of production and firms neither leaving nor entering the industry. A Decrease by 25 B Increase by 25 C Increase by 125 D Remain the same 7 7 Great Calls has D Remain the same. 54 If production increases by 25 how will total fixed costs likely react.
This preview shows page 4 - 6 out of 6 pages. C total product is increasing if marginal product is still positive D total product levels off 12. The type of cost behaviour 5.
Increase by 25 C. If production increases by 30 how will total variable costs likely react. Fixed cost per unit is 9 when 20000 units are produced and 6 when 30000 units are produced.
As production increases total variable costs increase at a decreasing rate since the marginal product for each additional worker is increasing. Since fixed costs do not change as output changes the total fixed cost line is flat at the level of fixed cost. What is the budgeted life-cycle cost per unit for product P.
It is also equal to the sum of average variable costs and average fixed costs. A Increase by 125 B Increase by 25 C Decrease by 25D Remain the same Answer. If at a given volume total costs and fixed costs are known the variable costs per unit may be computed as.
Fixed costs and variable costs affect the marginal cost of production only if variable costs exist. C Increasing marginal costs. If production increases by 25 how will total fixed costs likely react.
The average cost is the total cost divided by the number of goods produced. Thus Bikes Unlimited has total fixed costs of 20000 per month related to its production facility 8000 2000 6000 4000. What is the total fixed cost when nothing is produced.
In the Cost Theory there are two types of costs associated with production Fixed Costs and Variable Costs. The total cost of a business is composed of fixed costs and variable costs. All other fixed production costs total 4000.
The production function. How costs react to changes in profit. Remain the same 6.
B Decreasing marginal costs. Accounting questions and answers. B A period where the law of diminishing returns does not hold.
The companys total fixed production overheads are budgeted to be 72 million each year and total machine hours are budgeted to be 96 million hours. The marginal production i increases ii decreases and iii further. 2 50 100 150 25 500 75 20 3 65 100 165 217 333 55 15 4 77 100 177 193 250 443 12.
The marginal cost of. Total Cost Total Fixed Costs Total Variable Costs Opportunity Costs 14. If no production takes place variable costs are zero.
In addition insurance for the same building is 2000 per month and salaried production personnel are paid 6000 per month. Total fixed costs are the sum of all consistent non-variable expenses a company must pay. Given that total fixed costs TFC are constant as output increases the curve is a horizontal line on the cost graph.
The total cost TC curve is found by adding total fixed and total variable costs. Hence the total cost is increasing and linear in the production level. Increase by 125 B.
6 If production increases by 25 how will total fixed costs likely react. If production increases by 25 how will total fixed costs likely react O Decrease by 25 O Increase by 25 Remain the same Increase by 125. However the fixed cost per unit decreases as production increases because the same fixed costs.
Increased production will reduce the amount of fixed costs that need to be applied to each unit produced which will reduce the companys cost per unit. Fixed costs do not vary with the production level. D defined as the change in total cost resulting from the production of an additional unit of output.
August 01 2017. C costs that change with the level of production. D 64 The representation for total variable costs is A vx f.
Decreasing Sales Volume Decreasing sales volume will only decrease fixed unit costs when the quantity produced drops so low that production assets are sold or a less expensive facility is located.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_Does_Price_Elasticity_Affect_Supply_Feb_2020-02-9e07b9c680ac4926adba76eded63d372.jpg)
How Does Price Elasticity Affect Supply

Doc X03 Activity Costs Wp Bailabi Aquia Academia Edu

Final Exam Study Guide Acc 222 Intro To Managerial Accounting Studocu

Solved Which Of The Following Costs Change In To A Period Chegg Com
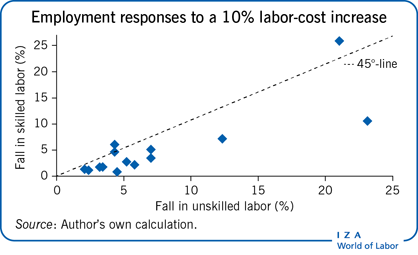
Iza World Of Labor Do Labor Costs Affect Companies Demand For Labor
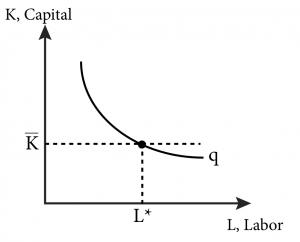
Module 7 Minimizing Costs Intermediate Microeconomics
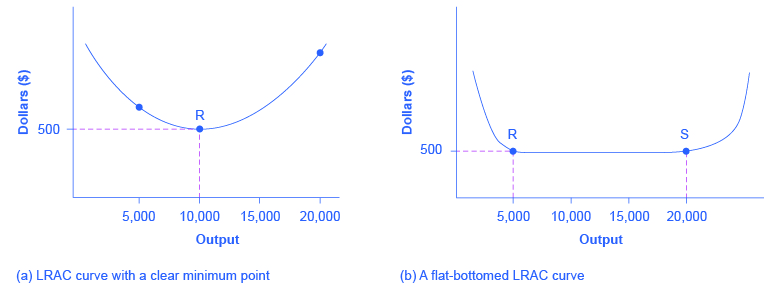
7 3 The Structure Of Costs In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
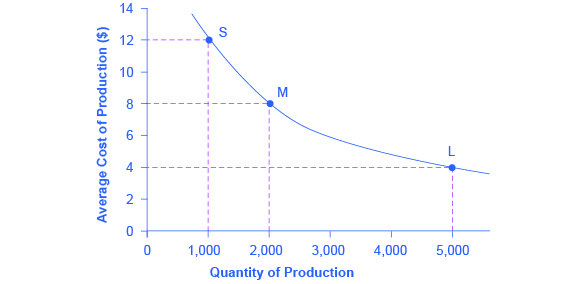
7 3 The Structure Of Costs In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
Costing Problems Cost Accounting Punjab University Studocu
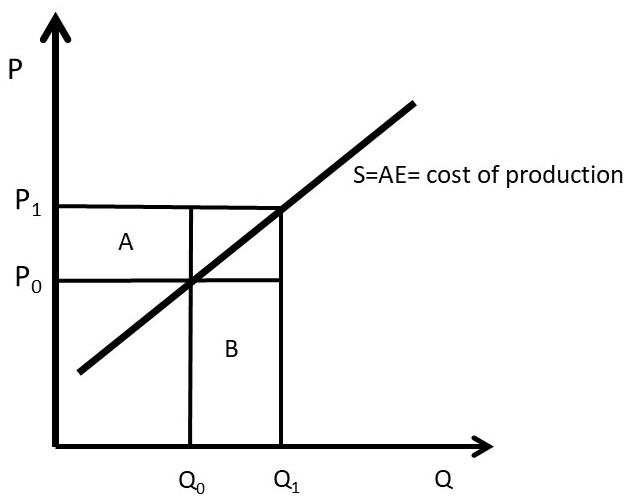
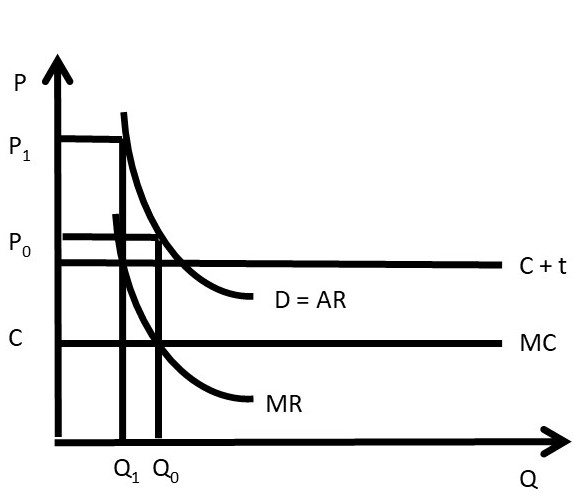
Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets

Break Even Analysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Break Even Analysis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
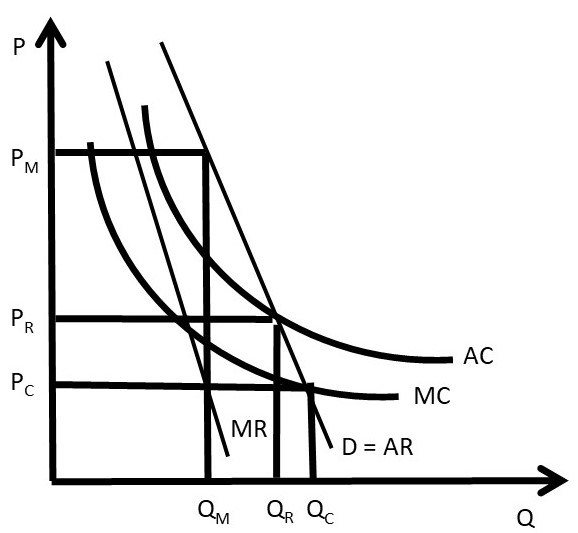
Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets
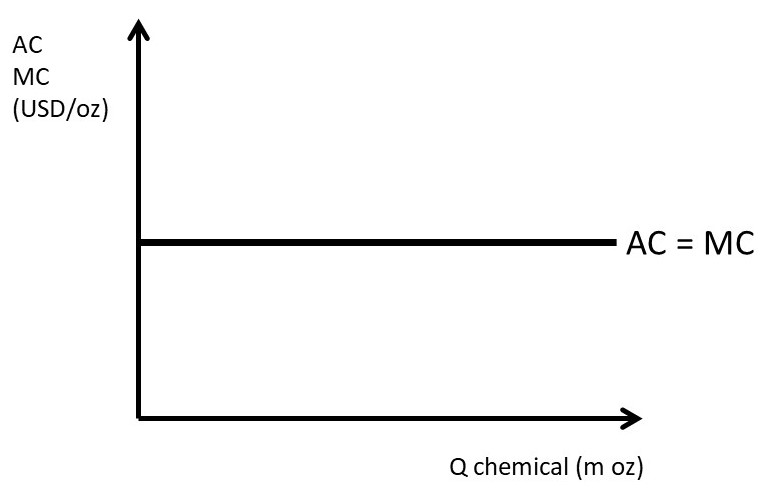
Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets
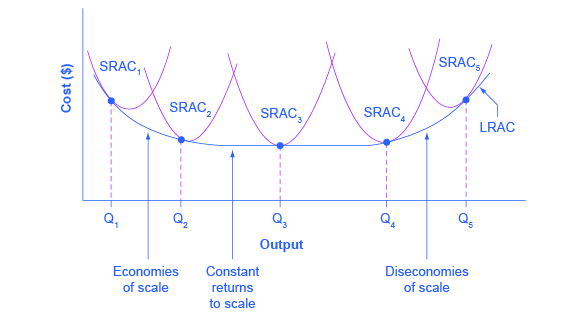
7 3 The Structure Of Costs In The Long Run Principles Of Economics
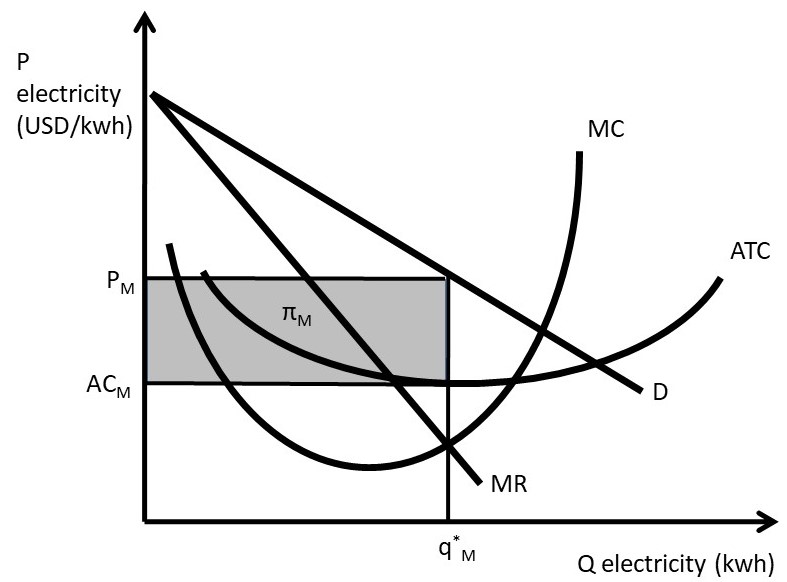
Chapter 5 Monopolistic Competition And Oligopoly The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets
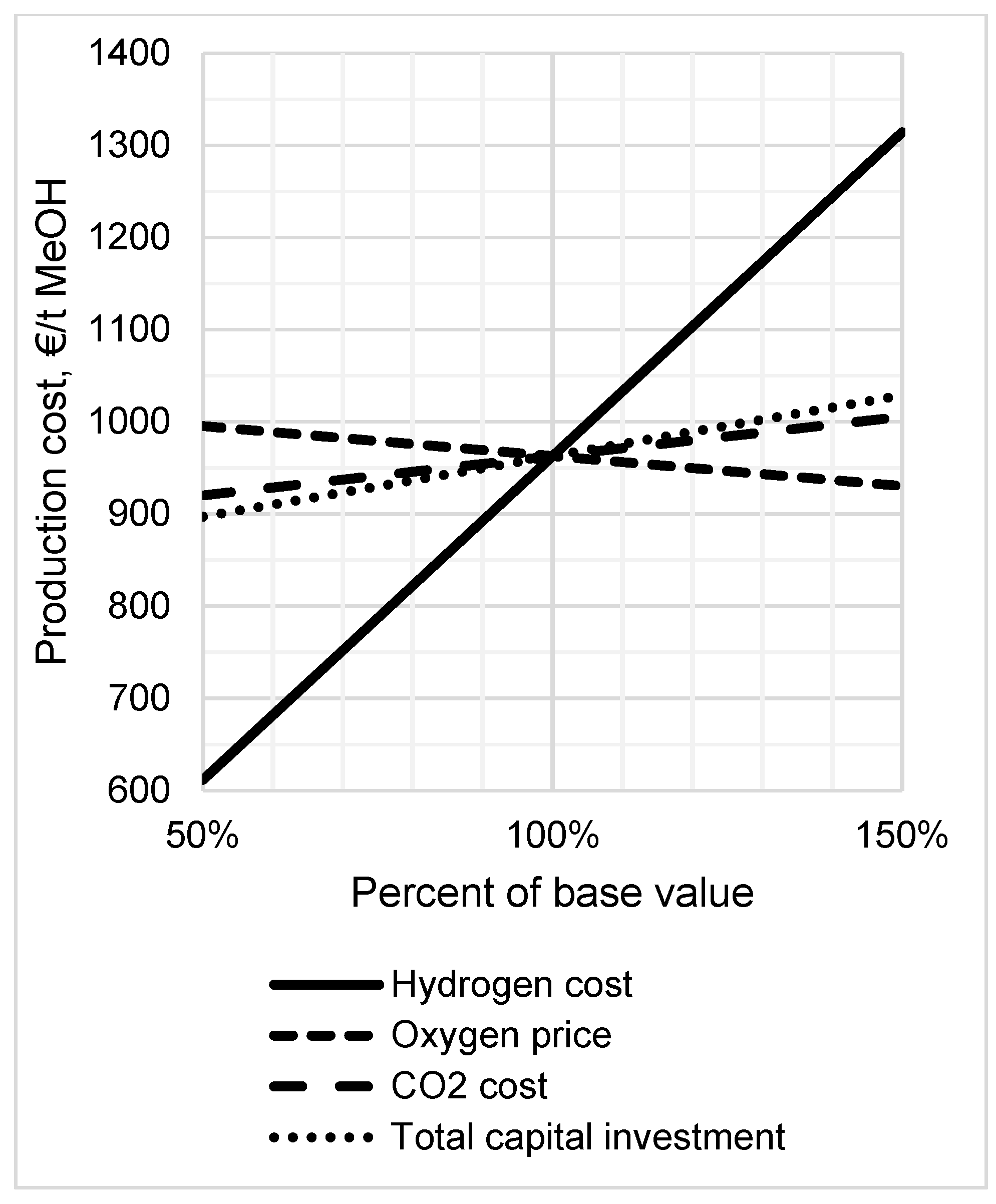
Processes Free Full Text Co2 Hydrogenation To Methanol By A Liquid Phase Process With Alcoholic Solvents A Techno Economic Analysis Html

Chapter 3 Monopoly And Market Power The Economics Of Food And Agricultural Markets

Post a Comment for "If Production Increases By 25%, How Will Total Fixed Costs Likely React?"